102 write_sysreg(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, MPIDR_EL1), vmpidr_el2);
105 !cpus_have_final_cap(ARM64_WORKAROUND_SPECULATIVE_AT)) {
106 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, SCTLR_EL1), SYS_SCTLR);
107 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, TCR_EL1), SYS_TCR);
108 }
else if (!ctxt->__hyp_running_vcpu) {
114 write_sysreg_el1((ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, TCR_EL1) |
115 TCR_EPD1_MASK | TCR_EPD0_MASK),
120 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, CPACR_EL1), SYS_CPACR);
121 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, TTBR0_EL1), SYS_TTBR0);
122 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, TTBR1_EL1), SYS_TTBR1);
123 if (cpus_have_final_cap(ARM64_HAS_TCR2))
124 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, TCR2_EL1), SYS_TCR2);
125 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, ESR_EL1), SYS_ESR);
126 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, AFSR0_EL1), SYS_AFSR0);
127 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, AFSR1_EL1), SYS_AFSR1);
128 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, FAR_EL1), SYS_FAR);
129 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, MAIR_EL1), SYS_MAIR);
130 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, VBAR_EL1), SYS_VBAR);
131 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, CONTEXTIDR_EL1), SYS_CONTEXTIDR);
132 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, AMAIR_EL1), SYS_AMAIR);
133 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, CNTKCTL_EL1), SYS_CNTKCTL);
134 if (cpus_have_final_cap(ARM64_HAS_S1PIE)) {
135 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, PIR_EL1), SYS_PIR);
136 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, PIRE0_EL1), SYS_PIRE0);
138 write_sysreg(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, PAR_EL1), par_el1);
139 write_sysreg(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, TPIDR_EL1), tpidr_el1);
142 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, TFSR_EL1), SYS_TFSR);
143 write_sysreg_s(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, TFSRE0_EL1), SYS_TFSRE0_EL1);
147 cpus_have_final_cap(ARM64_WORKAROUND_SPECULATIVE_AT) &&
148 ctxt->__hyp_running_vcpu) {
159 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, SCTLR_EL1), SYS_SCTLR);
161 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, TCR_EL1), SYS_TCR);
164 write_sysreg(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, SP_EL1), sp_el1);
165 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, ELR_EL1), SYS_ELR);
166 write_sysreg_el1(ctxt_sys_reg(ctxt, SPSR_EL1), SYS_SPSR);
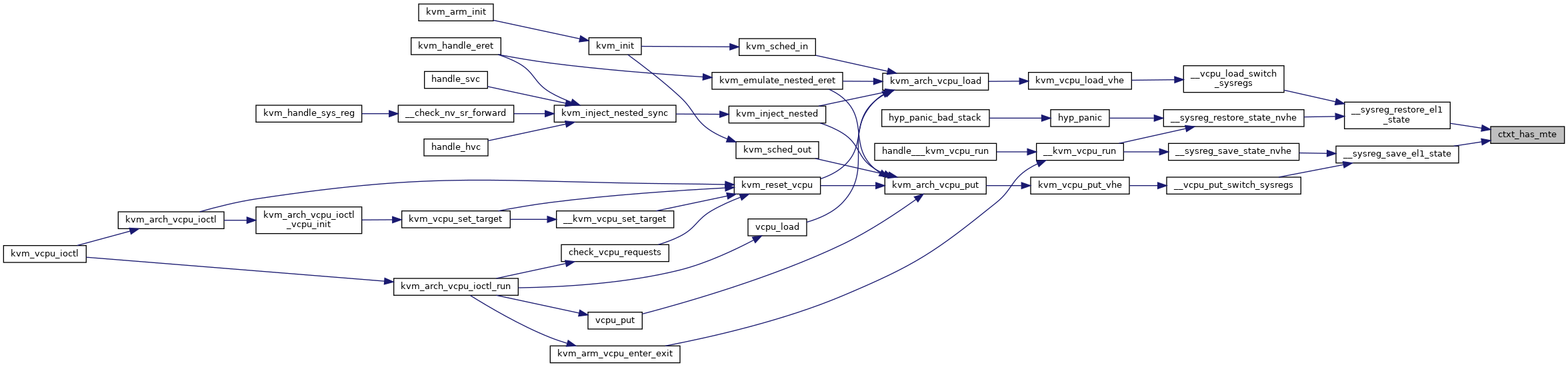
static bool ctxt_has_mte(struct kvm_cpu_context *ctxt)