#include <linux/kvm_host.h>#include <asm/kvm_emulate.h>#include <trace/events/kvm.h>#include "trace.h"
Include dependency graph for mmio.c:
Go to the source code of this file.
Functions | |
| void | kvm_mmio_write_buf (void *buf, unsigned int len, unsigned long data) |
| unsigned long | kvm_mmio_read_buf (const void *buf, unsigned int len) |
| int | kvm_handle_mmio_return (struct kvm_vcpu *vcpu) |
| int | io_mem_abort (struct kvm_vcpu *vcpu, phys_addr_t fault_ipa) |
Function Documentation
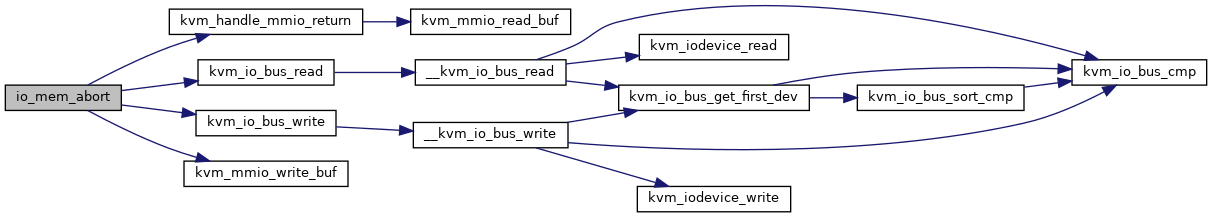
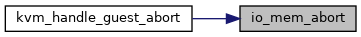
◆ io_mem_abort()
| int io_mem_abort | ( | struct kvm_vcpu * | vcpu, |
| phys_addr_t | fault_ipa | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 123 of file mmio.c.
int kvm_io_bus_read(struct kvm_vcpu *vcpu, enum kvm_bus bus_idx, gpa_t addr, int len, void *val)
Definition: kvm_main.c:5878
int kvm_io_bus_write(struct kvm_vcpu *vcpu, enum kvm_bus bus_idx, gpa_t addr, int len, const void *val)
Definition: kvm_main.c:5807
void kvm_mmio_write_buf(void *buf, unsigned int len, unsigned long data)
Definition: mmio.c:13
Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:
◆ kvm_handle_mmio_return()
| int kvm_handle_mmio_return | ( | struct kvm_vcpu * | vcpu | ) |
kvm_handle_mmio_return – Handle MMIO loads after user space emulation or in-kernel IO emulation
@vcpu: The VCPU pointer
Definition at line 81 of file mmio.c.
unsigned long kvm_mmio_read_buf(const void *buf, unsigned int len)
Definition: mmio.c:45
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:

◆ kvm_mmio_read_buf()
| unsigned long kvm_mmio_read_buf | ( | const void * | buf, |
| unsigned int | len | ||
| ) |